fasting insulin levels chart|Understanding Fasting Insulin Blood Test Results : Clark Fasting Insulin Levels Chart In the Fasting Insulin Levels Chart, age groups are categorized with their respective normal fasting insulin level ranges, measured in µIU/mL: Children (Age . Total War: Rome II (с англ. — «Тотальная война: Рим II») — компьютерная стратегическая игра, разработанная британской компанией Creative Assembly. Официально анонсирована 4 июля 2012 года [ 1]. Восьмая игра в серии Total War, сиквел и ремейк вышедшей в 2004 году игры Rome: Total War. Релиз игры .
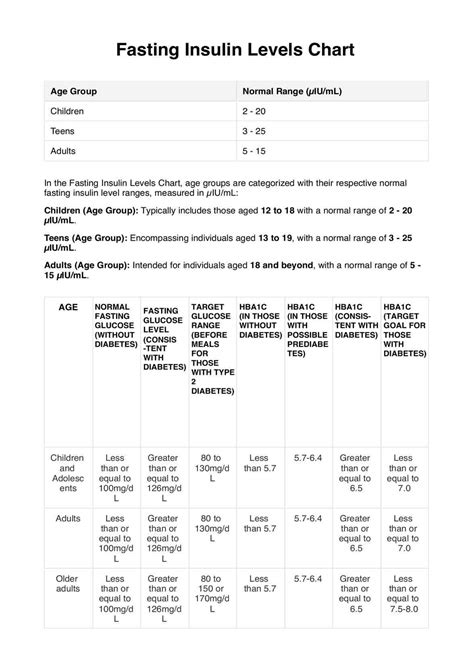
fasting insulin levels chart,Learn what fasting insulin is, why it is important, and how to interpret your results. Find out the causes and symptoms of low and high insulin levels, and how to improve your insulin health. Tingnan ang higit paInsulin is a hormone produced by beta cells in the pancreas. When you eat, your digestive system breaks down carbohydrates intoglucose, which is absorbed . Tingnan ang higit pa
This test measures the insulin levels in your blood after at least 8 hours of fasting. A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from your vein and send it to a lab for analysis. Other tests that may be performed to evaluate blood sugar and insulin . Tingnan ang higit paFasting insulin levels can serve as a tool to help guide the choice of therapy in patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. A study by Saxena et al found that such patients with normal.Fasting Insulin Levels Chart In the Fasting Insulin Levels Chart, age groups are categorized with their respective normal fasting insulin level ranges, measured in µIU/mL: Children (Age .

Learn how insulin regulates glucose, why fasting insulin tests are not standardized, and what are the possible indicators of insulin resistance. Find out how glucose levels can be used as a proxy for insulin sensitivity and how to .
fasting insulin levels chart Understanding Fasting Insulin Blood Test ResultsLearn how insulin regulates glucose, why fasting insulin tests are not standardized, and what are the possible indicators of insulin resistance. Find out how glucose levels can be used as a proxy for insulin sensitivity and how to . Learn what insulin sensitivity is, how it affects your blood sugar levels, and what factors can influence it. Find out how to diagnose low insulin sensitivity and what you can do to .Learn about insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and metabolism. Find out what insulin levels mean, how to interpret your lab results, and what causes insulin resistance and . Step 1: Obtain a template. Start by downloading this Fasting Insulin Levels Chart template for healthcare professionals from this page. Step 2: Record patient data. Enter the . Learn how fasting insulin tests offer personalized insights for improved health and lower your sugar levels. Find out the reference range, interpretation, and optimal levels for .
The fasting insulin test measures your insulin levels, which can indicate insulin resistance and pre-diabetes. Learn what optimal levels are, how to get the test, and what to do if your results are not ideal.
An insulin in blood test measures the amount of insulin in a sample of your blood. It can help diagnose or monitor conditions related to insulin, such as hypoglycemia, insulin . Maintaining insulin levels between 2.55 and 18.4 μIU/mL is generally recommended. [4] » Learn more about what to expect during a blood draw Interpreting fasting insulin blood test levels. A fasting insulin blood test should always accompany a fasting blood glucose test. Here’s how to interpret these test results. [1]Further analysis using the area under the curve revealed that at a fasting insulin level > 9.0 mIU/mL, prediabetes would be correctly identified in 80% of affected patients. A second model revealed that increased HOMA-IR index (OR = 1.303, CI = 1.205-1.410) and older age (OR = 1.037, CI = 1.024-1.05) predicted prediabetes. . Recommended blood sugar levels can help you know if your blood sugar is in a "normal" range. See the charts in this article for type 1 and type 2 diabetes for adults and children.

Glucose, Fasting 70-85 mg/dl optimal 85-100 mg /dl high 100-126 diabetes, prediabetes 126 plus indicative of diabetes Insulin Resistance Calculation (fasting insulin x fasting glucose) Divide that number by 405. If that calculation is greater than 1.8 you have insulin resistance. Leptin (use RIA testing) 4-6 ng/dl optimalUnderstanding Fasting Insulin Blood Test ResultsGlucose, Fasting 70-85 mg/dl optimal 85-100 mg /dl high 100-126 diabetes, prediabetes 126 plus indicative of diabetes Insulin Resistance Calculation (fasting insulin x fasting glucose) Divide that number by 405. If that calculation is greater than 1.8 you have insulin resistance. Leptin (use RIA testing) 4-6 ng/dl optimal
Women with 25 mcU/ml fasting insulin level had over 5 times the risk of prediabetes than women with 5 mcU/ml insulin level. Of course, the amount of insulin in the bloodstream will fluctuate in accordance with the levels of glucose. For more information on this, read the table below (information source: Medscape): . Other names: fasting insulin, insulin serum, total and free insulin. What is it used for? An insulin in blood test may be used with other tests to help: . If your insulin level is high and your blood glucose is normal or a little above normal for .fasting insulin levels chart One source lists normal ranges as either 5–15 or 5–12 mIU/L (30–90 or 30–78 pmol/L), depending on the test the doctor uses.. Also, health conditions such as obesity or diabetes can affect what a “normal” level might be. One small study from 2000 found that fasting insulin levels of participants without obesity were 5–7 mIU/L (30–42 pmol/L). In the long-term fasting state, insulin levels will continue to decrease and levels of beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), a type of ketone body, will steadily rise (1, 14).Fasting Insulin Levels Chart In the Fasting Insulin Levels Chart, age groups are categorized with their respective normal fasting insulin level ranges, measured in µIU/mL: Children (Age Group): Typically includes those aged 12 to 18 with a normal range of 2 - 20 µIU/mL.
Fasting insulin is between 3–8 uIU/mL (18–48 pmol/L). HgbA1C level is less than 5.6% (<37 mmol/mol). Glucose/insulin as HOMA-IR is near 1 (.5–1.5). Your total body fat is <28% for men and <32% for women. You show slight insulin resistance if . For this chart, we’ll assume that your premeal blood sugar target is 120 mg/dL and that 1 unit of fast-acting insulin will decrease your blood sugar by 50 points. Blood glucose 60–120 Blood sugar levels at least 8 hours after eating are important data points for people with and without diabetes. Clinical guidelines say they should generally be 90 to 130 mg/dL, but that may vary.
Your blood sugar increases with age, which raises the risk of type 2 diabetes for adults in their 50s, 60s, and 70s. Using a chart of blood sugar levels by age can help you track glucose. Blood sugar (glucose) targets for older people tend to be different than for younger people. Estimating the .
Age is just one factor that can impact glucose levels. Young children, teens, adults, and senior citizens may have different blood sugar goals. This chart details the clinical guidelines for . As the cells use the blood sugar, glucose and insulin levels in the blood decrease. But with diabetes, your body has trouble regulating glucose. Either your pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin, or your body doesn’t process insulin effectively. . This is a normal fasting blood sugar level. 100–125 mg/dL: Fasting blood sugar in this .
A fasting blood sugar test looks at a person's blood sugar levels to evaluate how well their body uses insulin. When someone eats, their blood sugar levels rise, and their body releases insulin. The insulin stores the sugar for energy later on. People who are diabetic or prediabetic do not make enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly.Daily time-restricted eating, or sometimes called the 16:8 plan, is fasting 16 hours and eating during an 8-hour period. For example, eating only during 12:00-8:00 p.m. Every other day or alternate-day fasting is eating one moderate-sized meal in the middle of the fast day and regular meals on the non-fasting day. An example of this is eating a .
Fasting glucose levels: between 72–85 mg/dL; 24-hour mean glucose levels: around 79–100 mg/dL; Mean post-meal glucose peaks: <110 mg/dL, with <30 mg/dL increase from pre-meal levels; Additionally, glucose levels should stay between 70 and 110 mg/dL for approximately 90 percent of the day (and rarely go above 140 mg/dL or below 60 mg/dL).
fasting insulin levels chart|Understanding Fasting Insulin Blood Test Results
PH0 · Understanding Your Lab Work: Fasting Insulin Test
PH1 · Understanding Fasting Insulin Blood Test Results
PH2 · Optimal Fasting Insulin Levels for Metabolic Health
PH3 · Insulin: Background, Serum Insulin Measurement, Interpretation
PH4 · Insulin in Blood: MedlinePlus Medical Test
PH5 · Insulin Sensitivity: What’s Low, High, and Normal?
PH6 · Insulin (Fasting)
PH7 · Fasting Insulin Test: Normal Range + Low & High Levels
PH8 · Fasting Insulin Levels Chart Guide
PH9 · Fasting Insulin Levels Chart